Alpha is a measure of the performance of an investment in relation to a benchmark index. Alpha will often be expressed in basis point terms, where 1 basis point is equal to one-hundredth of one percent i. It can also be regularly seen as a whole number — e. For a mutual fund that invests in mostly investment grade bonds, an aggregate bond index or associated ETF e. A close cousin of alpha, beta, is designed to measure systematic risk or volatility. Beta can be measured with respect to a single security — namely, its volatility relative to the broader market — or as it relates to an entire portfolio.
Total return is equal to the sum of alpha, beta, and whatever one returns on any cash holdings i. Alpha generation can also vary wildly depending on the business cycle. Portfolios invested exclusively in one type of asset class will disproportionately do well — even add alpha — in a specific type of market environment, but do poorly in another. Create a personalised ads profile.
Select personalised ads. Apply market research to generate audience insights. Measure content performance. Develop and improve products.
Lead Content
List of Partners vendors. Alpha is used in finance as a measure of performance , indicating when a strategy, trader, or portfolio manager has managed to beat the market return over some period. Alpha may be positive or negative and is the result of active investing. Beta, on the other hand, can be earned through passive index investing.
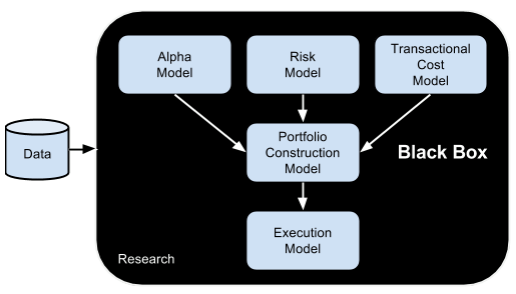
Create hundreds of new systematic trading strategies at the click of a button.
Alpha is one of five popular technical investment risk ratios. The others are beta, standard deviation , R-squared , and the Sharpe ratio. These are all statistical measurements used in modern portfolio theory MPT. All of these indicators are intended to help investors determine the risk-return profile of an investment. Active portfolio managers seek to generate alpha in diversified portfolios, with diversification intended to eliminate unsystematic risk. Because alpha represents the performance of a portfolio relative to a benchmark, it is often considered to represent the value that a portfolio manager adds to or subtracts from a fund's return.
In other words, alpha is the return on an investment that is not a result of a general movement in the greater market. As such, an alpha of zero would indicate that the portfolio or fund is tracking perfectly with the benchmark index and that the manager has not added or lost any additional value compared to the broad market.
These funds attempt to enhance the performance of a portfolio that tracks a targeted subset of the market. Despite the considerable desirability of alpha in a portfolio, many index benchmarks manage to beat asset managers the vast majority of the time. For investors, the example highlights the importance of considering fees in conjunction with performance returns and alpha. The Efficient Market Hypothesis EMH postulates that market prices incorporate all available information at all times, and so securities are always properly priced the market is efficient.
Therefore, according to the EMH, there is no way to systematically identify and take advantage of mispricings in the market because they do not exist.
Alpha Trading Strategies - Research | Savvy Investor
If mispricings are identified, they are quickly arbitraged away and so persistent patterns of market anomalies that can be taken advantage of tend to be few and far between. In other words, alpha is hard to come by, especially after taxes and fees. Because beta risk can be isolated by diversifying and hedging various risks which comes with various transaction costs , some have proposed that alpha does not really exist, but that it simply represents the compensation for taking some un-hedged risk that hadn't been identified or was overlooked.
- tier 1 covered options trading td ameritrade?
- Alpha Trading: Profitable Strategies That Remove Directional Risk | Wiley.
- Alternative Definitions of Alpha.
- Alpha Definition!
- Download Product Flyer.
Alpha is commonly used to rank active mutual funds as well as all other types of investments. Beta or the beta coefficient is used in the CAPM, which calculates the expected return of an asset based on its own particular beta and the expected market returns.
Example of alpha in finance
Alpha and beta are used together by investment managers to calculate, compare, and analyze returns. The entire investing universe offers a broad range of securities, investment products, and advisory options for investors to consider. Different market cycles also have an influence on the alpha of investments across different asset classes. This is why risk-return metrics are important to consider in conjunction with alpha.
FX Alpha Trading Strategies
It tracks a customized index called the Bloomberg Barclays U. Year-to-date, as of November 15, , its return was The Bloomberg Barclays U. Aggregate Index had a return of 3. Therefore, the alpha for ICVT was Aggregate Index and for relatively low risk with a standard deviation of 4. However, since the aggregate bond index is not the proper benchmark for ICVT it should be the Bloomberg Barclay's Convertible index , this alpha may not be as large as initially thought; and in fact, may be misattributed since convertible bonds have far riskier profiles than plain vanilla bonds. The WisdomTree U.
Its holdings track a customized index called the WisdomTree U. Quality Dividend Growth Index. Its annualized return as of November 15, , was The above example illustrates the success of two fund managers in generating alpha. When using a generated alpha calculation it is important to understand the calculations involved.
- registered forex brokers india?
- positive expectancy forex system;
- examples of option trading.
- Description?
- forex real profit ea;
Alpha can be calculated using various different index benchmarks within an asset class. In some cases, there might not be a suitable pre-existing index, in which case advisors may use algorithms and other models to simulate an index for comparative alpha calculation purposes. Alpha can also refer to the abnormal rate of return on a security or portfolio in excess of what would be predicted by an equilibrium model like CAPM.