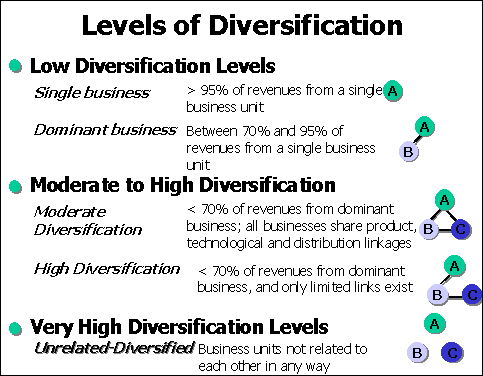
Diversification strategies help to increase flexibility and maintain profit during sluggish economic periods. A concentric diversification strategy lets a firm to add similar products to an already established business. For example, when a computer company producing personal computers using towers starts to produce laptops, it uses concentric strategies. The technical knowledge for new venture comes from its current field of skilled employees.
Concentric diversification strategies are rampant in the food production industry. For example, a ketchup manufacturer starts producing salsa, using its current production facilities. Horizontal diversification allow a firm to start exploring other zones in terms of product manufacturing. Companies depend on current market share of loyal customers in this strategy. When a television manufacturer starts producing refrigerators, freezers and washers or dryers, it uses horizontal diversification.
The company has to leverage on the brand loyalty associated with current products. In conglomerate diversification strategies, companies will look to enter a previously untapped market. This is often done using mergers and acquisitions. Moving into a new industry is highly dangerous, due to unfamiliarity with the new industry.
Other acquisitions fail because the buyer pays more for a target company than that company is worth and the buyer never earns back the premium it paid. Thus, executives need to be cautious when considering using horizontal integration. When pursuing a vertical integration strategy, a firm gets involved in new portions of the value chain Table 8. By entering the domain of a supplier or a buyer, executives can reduce or eliminate the leverage that the supplier or buyer has over the firm.
Firms can pursue vertical integration on their own, such as when Apple opened stores bearing its brand, or through a merger or acquisition, such as when eBay purchased PayPal. In the late s, Carnegie Steel Company was a pioneer in the use of vertical integration. The firm controlled the iron mines that provided the key ingredient in steel, the coal mines that provided the fuel for steel making, the railroads that transported raw material to steel mills, and the steel mills themselves.
CONGLOMERATE DIVERSIFICATION
Having control over all elements of the production process ensured the stability and quality of key inputs. By using vertical integration, Carnegie Steel achieved levels of efficiency never before seen in the steel industry. When using vertical integration, firms get involved in different elements of the value chain. Today, oil companies are among the most vertically integrated firms. Firms such as ExxonMobil and ConocoPhillips can be involved in all stages of the value chain, including crude oil exploration, drilling for oil, shipping oil to refineries, refining crude oil into products such as gasoline, distributing fuel to gas stations, and operating gas stations.
The risk of not being vertically integrated is illustrated by the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Although the US government held BP responsible for the disaster, BP cast at least some of the blame on drilling rig owner Transocean and two other suppliers: Halliburton Energy Services which created the cement casing for the rig on the ocean floor and Cameron International Corporation which had sold Transocean blowout prevention equipment that failed to prevent the disaster. In April , BP sued these three firms for what it viewed as their roles in the oil spill.
Vertical integration also creates risks. Venturing into new portions of the value chain can take a firm into very different businesses. A lumberyard that started building houses, for example, would find that the skills it developed in the lumber business have very limited value to home construction. Such a firm would be better off selling lumber to contractors. Vertical integration can also create complacency. Consider, for example, a situation in which an aluminum company is purchased by a can company.
People within the aluminum company may believe that they do not need to worry about doing a good job because the can company is guaranteed to use their products. Some companies try to avoid this problem by forcing their subsidiary to compete with outside suppliers, but this undermines the reason for purchasing the subsidiary in the first place. Some firms use this strategy when executives are concerned that a supplier has too much power over their firms. In the early days of the automobile business, Ford Motor Company created subsidiaries that provided key inputs to vehicles such as rubber, glass, and metal.
This approach ensured that Ford would not be hurt by suppliers holding out for higher prices or providing materials of inferior quality.
Although backward vertical integration is usually discussed within the context of manufacturing businesses, such as steel making and the auto industry, this strategy is also available to firms such as Disney that compete within the entertainment sector. Rather than depend on outside production companies to provide talk shows and movies centered on sports, ESPN created its own production company. By owning its own production company, ESPN can ensure that it has a steady flow of programs that meet its needs.
This allows Disney to capture profits that would otherwise be enjoyed by another store.
8.4 Diversification Strategies
Each time a Frozen book bag is sold through a Disney store, the firm makes a little more profit than it would if the same book bag were sold by a retailer such as Target. Forward vertical integration also can be useful for neutralizing the effect of powerful buyers. Rental car agencies are able to insist on low prices for the vehicles they buy from automakers because they purchase thousands of cars.
If one automaker stubbornly tries to charge high prices, a rental car agency can simply buy cars from a more accommodating automaker. This ensured that Hertz would not drive too hard of a bargain when buying Ford vehicles. By , selling vehicles to rental car companies had become less important to Ford and Ford was struggling financially. The firm then reversed its forward vertical integration strategy by selling Hertz. Despite its enormous success, one concern for eBay is that many individuals avoid eBay because they are nervous about buying and selling goods online with strangers. PayPal addressed this problem by serving, in exchange for a fee, as an intermediary between online buyers and sellers.
Employees at Best Buy and Office Depot are likely to know only a little bit about each of the various brands their store carries. They can therefore provide customers with accurate and insightful advice about purchases and repairs. This is an important advantage that has been created through forward vertical integration. Henry, D. Business Week , 60— Lakelet Capital.
Porter, M. From competitive advantage to corporate strategy. Harvard Business Review , 65 3 , — Prahalad, C. The core competencies of the corporation. Harvard Business Review , 86 1 , 79— Associated Press. The Daily Journal. Wagenheim, J. UFC buys out Strikeforce in another step toward global domination. Sports Illustrated. Figure 8. Image of perfume: Dhini van Heeren Retrieved from: flic. Image of Compact: Kindred Grey Public Domain.
Image of Lipstick: eleni koureas Adaptation of Figure 8. Retrieved from flic. Retrieved from en. Three Tests for Diversification A proposed diversification move must first answer three questions to determine if it should be accepted or rejected Porter, How attractive is the industry that a firm is considering entering? Unless the industry has strong profit potential, entering it may be very risky. How much will it cost to enter the industry?
Executives need to be sure that their firm can recoup the expenses that it absorbs in diversifying. When Philip Morris bought 7Up, it paid four times what 7Up was actually worth. Making up these costs proved to be impossible and 7Up was sold less than 10 years later. Will the new unit and the firm be better off? Unless at least one side gains a competitive advantage, diversification should be avoided. In the case of Philip Morris and 7Up, for example, neither side benefited significantly from joining together. Table 8. They maintain capital strength at exceptionally high levels, which gives them an advantage even a caveman could understand.
Their apparel businesses include well-known names such as Fruit of the Loom and Justin Brands.
What you need to know about diversification, a key growth strategy – Berley Chartered Accountants
FlightSafety International Inc. Retail holdings include a number of furniture businesses such as R. Shareholders were all on board for the purchase of the Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation railroad in Geographic Diversification Firms may also diversify through expanding geographically. Horizontal Integration: Mergers and Acquisitions Horizontal integration refers to pursuing a diversification strategy by acquiring or merging with a rival.
It was formed by the merger of Exxon and Mobil.
As in many mergers, the new company name combines the old company names. HP has pursued horizontal integration through a merger with Compaq computers and the acquisition of Palm, a digital personal assistant. Both failed miserably. The marriage failed, with billions of dollars in losses, and Chrysler is currently owned by Italian automaker Fiat.
There tend to be many of mergers in the banking industry. The merger of wireless carriers Sprint and T-Mobile combined the number three and four companies in the market.
- forex swap fee.
- auditing stock options;
- options trading intrinsic value.
- forex game app.
The new company name dropped Sprint and operates under the name T-Mobile. Vertical Integration Strategies When pursuing a vertical integration strategy, a firm gets involved in new portions of the value chain Table 8. Manufacturing is conducted in an , square foot factory in downtown Los Angeles.