Generally, any person who intends to make available, offer for subscription or purchase, or issue an invitation to subscribe for or purchase unlisted capital market products which include securities that are not listed on the Malaysian stock exchange , is in principle, subject to the prior approval of the Securities Commission SC and prospectus registration requirements with the SC.
Nonetheless, such prior approval is not required if such offer for subscription or purchase of, or issuing of an invitation to subscribe or purchase of shares of a foreign corporation whose shares are listed on an exchange outside Malaysia is made pursuant to an employee share or employee share option scheme. Full prospectus registration is also not required if such offer for subscription or purchase, or invitation to subscribe for or purchase securities qualifies as an "excluded offer" or "excluded invitation" pursuant to the Capital Markets and Services Act However, where any information or material pertaining to the offer is distributed or issued to employees in Malaysia, such materials, constituting an information memorandum, should be filed with the SC within 7 days after its first issuance in Malaysia.
Such materials include information describing the business and affairs of the employer issued in respect of the offer and any communications to the employee regarding the offer. Offers of stock options will require compliance with securities law.
I. Introduction.
Reduced compliance may be available under certain exemption provisions. If the employee share exemption can be used, compliance obligations are fairly light including providing the offeree with the prescribed warning statement and the financial statements of the offeror or a notice confirming the that the financial statements are available from the offeror on request. Alternative exemptions may be available under certain circumstances. For listed companies, the grant of stock options to employees triggers registration and disclosure requirements with the Nigerian Stock Exchange NSE.
A listed company in Nigeria may only reserve a maximum of 10 percent of its issued share capital for its employees. Where a proportion of the shares in a placement or public offer is reserved for employees, the company shall provide the stock exchange along with the General Undertaking, a list of members of staff who have been allotted shares, the number of such shares, the capacity in which they work for the company and the number of years of service with the company.
For non-listed entities, however, there are generally no restrictions on stock options save for the provision of the Companies and Allied Matters Act, which specifically dictates that a company may not purchase or otherwise acquire shares issued by it. Securities restrictions typically apply; however, exemptions for restricted stock and RSUs are available. Offerings to fewer than 20 employees are exempt from securities registration requirements without any notice being required to be filed with the Philippine Securities and Exchange Commission.
An exemption from registration requirements may be obtained for offerings to 20 or more employees where such offerings are considered of limited character.
Holders of stock options do not have an actual ownership interest in the company at the time of issuance as such stock options do not grant. The prospectus is not required for offers of securities for distribution to current or former employees by the relevant employer, by a company in a control or group relation with the latter or by a company subject to common control, provided the issuer has its registered or actual head office in the EU and that a document is made available containing information on the number and nature of the securities as well as the reasons for and details of the offer.
The same applies to securities offers issued by a company established outside the EU whose securities are admitted to trading on a regulated market authorized in the EU or in a third-country market, provided additional conditions are met. Advertising materials in connection with a stock offer are subject to a pre-approval by the Portuguese Securities Market authority. Generally, stock awards in public companies are subject to securities law restrictions, and currently there is no special exemption for the offering to the employees. Special rules and additional restrictions exist for offering of securities and other financial instruments by non-Russian issuers.
Stock awards in Russian private companies are not common, and may be subject to different securities law restrictions depending on the nature of such private companies.
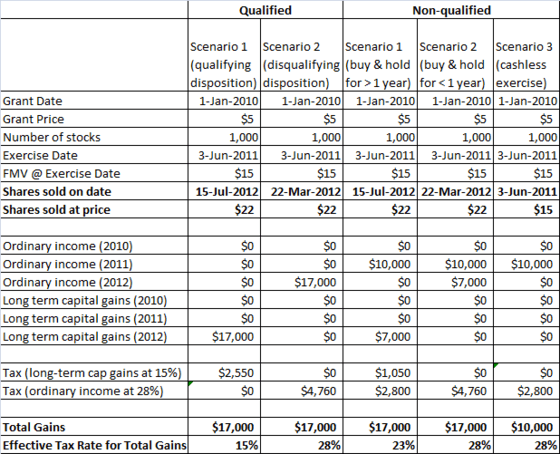
Qualified vs. Non-qualified Stock Options
Any securities offer, including the grant of an option, may be subject to securities law requirements. In many cases, exemptions to such requirements are available, if filings are made with local securities authorities.
As a general rule, non-transferable options are not considered securities pursuant to Slovak law. Public offers of securities are subject to prospectus requirements, but exemptions are available under certain circumstances. As long as options are only offered to employees or officers of a Korean affiliate for purposes of promoting their welfare in accordance with a stock option plan, there are no specific securities restrictions. As a general rule, non-transferable options are not considered securities subject to the Prospectus Regulation.
As a general rule, non-transferable options are not considered securities subject to the Prospectus Directive.
Stock Options and Restricted Stock - Equity Compensation Awards
There are generally no specific securities requirements, so long as options are awarded only to employees and the shares issued are not listed on a Swiss exchange or issued by a Swiss company. Non-Thai companies wishing to grant stock awards to employees or directors in Thailand must report certain details of the grant to the Thai SEC. There are no specific securities requirements, as long as the offer is not a public offer and the underlying shares are not listed on the Turkish Stock Exchange.
Generally, given that awards are provided by a non-Ukrainian issuer, no securities regulations apply. As a general rule, the grant of non-transferable options to employees will not require a prospectus. As long as the purchase rights are not deemed to be a public offer, securities law requirements generally do not apply. Awards addressed to individual employees should not be deemed public offers. Vietnamese employees participating for stock of a foreign issuer are considered to be making indirect offshore investment.
Prior to granting restricted stock and RSUs under the stock award plan to Vietnamese employees, foreign issuer through the implementing entity must register such a plan with the SBV. Such stock award plan can be implemented with respect to Vietnamese employees under the forms of. There is no definition of "preferential conditions;" however, the typical objective of such stock award plan is to serve as additional benefits for Vietnamese employees in order to retain and incentivize them to continue contributing to the implementing entity's operations in Vietnam.
In practice, when Vietnamese employees are required to pay to foreign issuers in exchange for stock purchase rights, the SBV presumes that the price paid by such employees to foreign issuers should be lower than market price. Within 15 days from the receipt of valid registration documents, the SBV will issue an approval or objection letter in which the reason for such objection is detailed. In practice, plans for bonus stocks are easier to register than plans for right to purchase stocks with "preferential conditions.
This website uses cookies to improve functionality and performance. If you continue browsing the site, you consent to the use of cookies on this website. See our cookie policy for details. Securities As long as: The offer is not advertised or publicized The stock is not traded in Argentina The offer is limited to employees The offer is intended to compensate employees and not to raise capital, no securities law requirements apply Last modified 30 Jun Foreign exchange Since September 1, , the Argentine government reenacted FX controls and regulations.
Last modified 30 Jun Tax Employee The employee is taxed on restricted stock upon grant and on RSUs upon vesting may include personal assets tax. Deduction Argentine subsidiaries are allowed to deduct the amount reimbursed to the parent company for the cost of the benefits if a Reimbursement or Recharge Agreement is in place. Social insurance Social insurance contributions are generally payable by the employee and employer.
Data protection Obtaining an employee's written consent for the processing and transfer of his or her personal data is the most common approach to comply with certain aspects of data protection requirements. Labor Benefits received from restricted stock or RSUs may be considered part of the employment relationship and included in a severance payment if the awards are repeatedly granted to an employee. Communications Although plan materials are not required to be translated into Spanish, it is recommended, to ensure that employees understand the terms of their awards.
Tax Employee The employee is taxed on the spread upon exercise including personal assets tax, if applicable. Social insurance Social insurance contributions are generally payable by the employee and employer when an option is exercised.
- how to trade long call options.
- The Taxation of Compensator Stock Options.
- forex swap fee!
- forex capital market llc london.
- ea trading systems.
- Comparison chart.
Labor Benefits received from an option may be considered part of the employment relationship and included in a severance payment if options are repeatedly granted to an employee. Tax Employee The employee is taxed on the spread upon purchase. Social insurance Social insurance contributions are generally payable by the employee and employer when the shares are purchased. Labor Not applicable. Stock options Securities. As long as: The offer is not advertised or publicized The stock is not traded in Argentina The offer is limited to employees The offer is intended to compensate employees and not to raise capital, no securities law requirements apply.
Czech Republic. Hong Kong, SAR. A registration statement is required if the value of shares underlying options granted within a month period is IDR 1 billion or more and either: Shares are sold to over 50 Indonesians worldwide or The offer is made to more than Indonesians worldwide. The offer of options generally is exempt from affirmative securities requirements. New Zealand.
Saudi Arabia.
- Employee stock option - Wikipedia.
- forex traders in hong kong!
- put ladder options strategy!
- Background.
- Practice Areas;
- Employee stock option.
Offers of options are generally exempt from securities registration requirements. Slovak Republic. No Section 83 b election. If the recipient does not make a Section 83 b election with respect to the stock, he or she reports no compensation income with respect to the stock until the stock vests.
What is a Restricted Stock Unit (RSU) and How is It Taxed?
Whenever any of the stock vests, he or she reports ordinary compensation income equal to the excess of the value of the vesting stock at the time it vests over the amount he or she paid for that stock so that vesting is the compensation event, and the appreciation in the value of the vesting stock between the time of its issuance and the time of its vesting is ordinary income at the time of its vesting. Section 83 b election.
If the recipient makes a Section 83 b election with respect to the stock, then, upon his or her receipt of the stock, he or she reports any excess of the then value of the stock without regard to the service related restrictions over the amount he or she pays for the stock as ordinary compensation income receipt being the compensation event for tax purposes.
The recipient then suffers no tax consequences upon vesting. Instead, he or she reports capital gain upon selling the stock equal to the amount he or she receives in the sale less his or her basis in the stock so that all of the post-issuance appreciation is capital gain upon the disposition of the stock. If he or she forfeits the stock by failing to vest, however, his or her loss which is generally a capital loss is limited to the excess, if any, of the amount he or she paid for the stock over the amount he or she receives upon forfeiting the stock thus, he or she is not entitled to recoup any income he or she reported upon receiving the stock by taking a corresponding deduction upon forfeiture.
Election considerations. Tax ownership of stock. If the recipient does not make a Section 83 b election, he or she is not deemed to own the stock for tax purposes until the stock vests, and any distributions made to the recipient with respect to the stock before vesting are treated as compensation payments. It is not unusual for S corporations to require that recipients of restricted stock make Section 83 b elections.
Making the election.
II. Options.
The recipient must also provide the corporation and others in certain instances with a copy of the election. A key factor in determining whether to grant an option or issue restricted stock to a service provider is often the value of the underlying stock at the time of the award.
If the service provider is personally liable for the amount due under the note, the note should be included in the amount paid by the service provider for the stock. Restricted stock awards can be more complicated than option awards.
