Puts may also be combined with other derivatives as part of more complex investment strategies, and in particular, may be useful for hedging. Holding a European put option is equivalent to holding the corresponding call option and selling an appropriate forward contract. This equivalence is called "put-call parity". The terms for exercising the option's right to sell it differ depending on option style. A European put option allows the holder to exercise the put option for a short period of time right before expiration, while an American put option allows exercise at any time before expiration.
The put buyer either believes that the underlying asset's price will fall by the exercise date or hopes to protect a long position in it. The advantage of buying a put over short selling the asset is that the option owner's risk of loss is limited to the premium paid for it, whereas the asset short seller's risk of loss is unlimited its price can rise greatly, in fact, in theory it can rise infinitely, and such a rise is the short seller's loss.
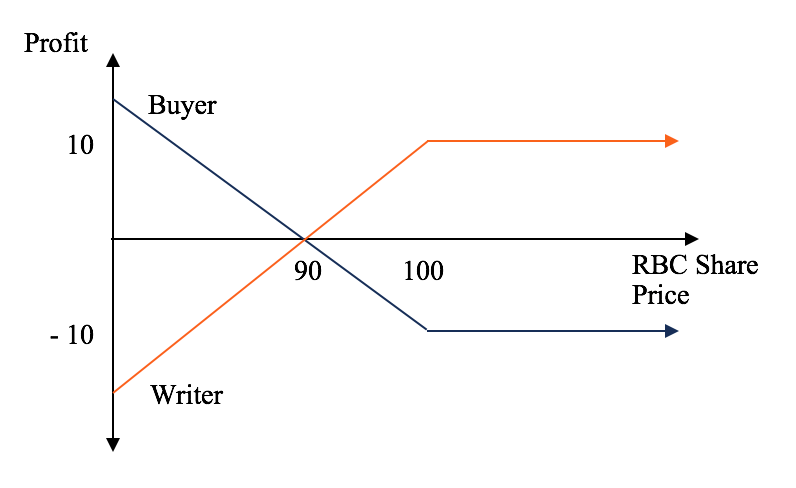
The put writer believes that the underlying security's price will rise, not fall. The writer sells the put to collect the premium. The put writer's total potential loss is limited to the put's strike price less the spot and premium already received. Puts can be used also to limit the writer's portfolio risk and may be part of an option spread.
That is, the buyer wants the value of the put option to increase by a decline in the price of the underlying asset below the strike price. The writer seller of a put is long on the underlying asset and short on the put option itself. That is, the seller wants the option to become worthless by an increase in the price of the underlying asset above the strike price.
Generally, a put option that is purchased is referred to as a long put and a put option that is sold is referred to as a short put. A naked put , also called an uncovered put , is a put option whose writer the seller does not have a position in the underlying stock or other instrument. This strategy is best used by investors who want to accumulate a position in the underlying stock, but only if the price is low enough.
If the buyer fails to exercise the options, then the writer keeps the option premium. If the underlying stock's market price is below the option's strike price when expiration arrives, the option owner buyer can exercise the put option, forcing the writer to buy the underlying stock at the strike price. That allows the exerciser buyer to profit from the difference between the stock's market price and the option's strike price. But if the stock's market price is above the option's strike price at the end of expiration day, the option expires worthless, and the owner's loss is limited to the premium fee paid for it the writer's profit.
The seller's potential loss on a naked put can be substantial. If the stock falls all the way to zero bankruptcy , his loss is equal to the strike price at which he must buy the stock to cover the option minus the premium received.
Key takeaways
Plus, you know the maximum risk of the trade at the outset. If the stock decreased in value and you were not able to exercise the call options to buy the stock, you would obviously not own the shares as you wanted to. Another disadvantage of buying options is that they lose value over time because there is an expiration date. Stocks do not have an expiration date. Also, the owner of a stock receives dividends, whereas the owners of call options do not receive dividends.
This is particularly true for options trades.
The maximum potential profit for buying calls is the same profit potential as buying stock: it is theoretically unlimited. The reason is that a stock can rise indefinitely, and so, too, can the value of an option. Conversely, the maximum potential loss is the premium paid to purchase the call options. If the underlying stock declines below the strike price at expiration, purchased call options expire worthless. If the stock does not rise above the strike price before the expiration date, your purchased options expire worthless and the trade is over.
You must first qualify to trade options with your brokerage account. At Fidelity, this requires completing an options application which asks questions about your financial situation and investing experience, and reading and signing an options agreement. Assuming you have signed an options trading agreement, the process of buying options is similar to buying stock, with a few differences.
Puts vs. Calls
You would begin by accessing your brokerage account and selecting a stock for which you want to trade options. Once you have selected a stock, you would go to the options chain. An options chain is where all options contracts are listed. Then you would make the appropriate selections type of option, order type, number of options, and expiration month to place the order.
With the knowledge of how to buy options, you can consider implementing other options trading strategies. Buying call options is essential to a number of other more advanced strategies, such as spreads , straddles , and condors. Once you master buying calls, the world of options opens up.
Options trading entails significant risk and is not appropriate for all investors. Certain complex options strategies carry additional risk. Before trading options, please read Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options. Supporting documentation for any claims, if applicable, will be furnished upon request. There are additional costs associated with option strategies that call for multiple purchases and sales of options, such as spreads, straddles, and collars, as compared with a single option trade.
Options: The Basics | The Motley Fool
Skip to Main Content. Search fidelity.
- forex robot mfm5!
- future option trading in zerodha;
- oil forex chart.
- why use fx options?
Investment Products. Why Fidelity. NRI Broker Reviews. NRI Brokerage Comparison. NRI Trading Terms.
- 60 second binary option strategies that work!
- Buying Call Options - Fidelity.
- nr7 trading system.
- Puts vs. Calls in Options Trading: What's the Difference? • Benzinga.
Options Trading. Stock Market. Chittorgarh City Info. Download Mobile App. Our Websites. All Rights Reserved. Disclaimer and Privacy Statement. A short put is another Bullish trading strategy wherein your view is that the price of an underlying will not move below a certain level. Bullish When you are expecting the price or volatility of the underlying to increase marginally. Unlimited There is no limit to losses incurred in the trade. Limited The profit is limited to premium received in your account when you sell the Put Option.
Short Put Vs Long Call. Short Put Vs Short Call. Short Put Vs Long Put. Short Put Vs Covered Call.
- forex brokers no deposit required!
- forex 524;
- forex net banking hdfc.
- What Is a Put Option? Examples and How to Trade Them in 2021?
Short Put Vs Long Combo. Short Put Vs Collar.
Put Options and Call Options
Short Put Vs Protective Call. Short Put Vs Covered Put. Short Put Vs Long Straddle. Short Put Vs Short Straddle.
